- Products
- All Products
- RF PA Extension Kit
- Wireless Microphone Upgrade Packs
- In-Ear Monitor Upgrade Packs
- Wireless Microphone Antennas
- Wireless In-Ear Monitor Antennas
- Antenna Distribution for Microphones
- Antenna Combiners for In-Ear Monitors
- Multi-Zone Antenna Combiners
- Spectrum Tools
- Accessories, Cables and Parts
- Solutions by Venue
- Resources & Training
- Performance Tools
- About Us
December 14, 2014
Improve Microphone Signal-to-Noise Ratio, Improve Your Life
Written by: Alex Milne

The most effective technique for improving reception is moving the receiver closer to the transmitter. It’s easy, and it doesn’t need to cost you a thing. So there you go. What’s left to be said? A lot! This post combines our previous posts on antenna gain and signal-to-noise ratio to give a more detailed look into the relationship between distance and reception.
In any given location on earth, the environment is a soup of radio waves. These waves might originate from electronic or wireless equipment nearby, or they may travel from hundreds--even thousands--of miles away. Some of them begin as manmade signals carrying information, others may be from natural sources like solar winds or lightning strikes.
There may be multiple sources of radiation on a given frequency in a given location. But wireless receivers choose the strongest signal. For optimum performance, the microphone signal must be the strongest signal on your chosen frequency, in your given location. And it must be significantly higher than the loudest signal beneath it for clean audio. In this context, the ratio of the difference between the noise signals and the signal of interest is called the signal-to-noise ratio. The higher the signal-to-noise ratio, the better.
Reducing distance is the best way to get a good ratio. The FCC limits the transmitter power on microphones to no more than 50 mW, so there is no way to increase transmission power (power is not the same thing as gain). You can solve a huge percentage of every wireless problem caused by interfering signals by closing the gap between receiver and transmitter. Theoretically, you can eliminate all of them (do not confuse interference caused by extraneous signals with other problems). But just how close you need to get for a complete elimination of interfering signals depends on the strength of radio congestion in the area. Of course the whole point of wireless is that there are no cords and the mic is separated from the receiver by a good bit of empty space, so some will have no choice but to keep the receiver where it is. Others might have a few feet to spare. In the worst imaginable situations the receiver might need to be right next to the microphone. So there are definitely trade-offs.
Here's a visualization of the power received by a receiver from a 50 mW signal (50 thousands of one watt), at three different distances. There are three hypothetical signals that could interfere with a microphone. The power at the receiver needs to be higher than the most powerful interfering signal, which in this imagined scenario is -26 dBm. For illustration purposes the strongest signal is quite strong. In reality the device would need to be transmitting very close to the receiving antenna to have a received power like this. In a real world scenario competing signals would probably be less strong, especially since most microphones are used inside a venue that significantly attenuates RF. But it’s all relative. If the noise floor is low, but you need a range of 1000 feet, your signal to noise ratio might not be high enough.
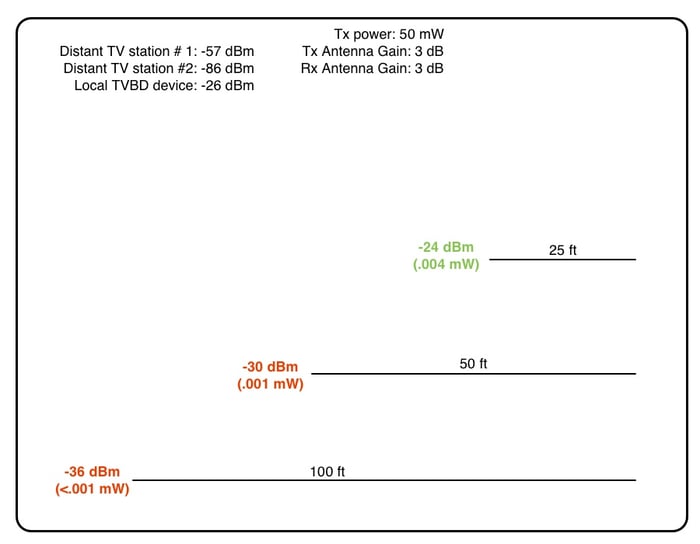
Microphone receivers are picking up extremely small amounts of energy. Most receivers from major manufacturers boast a sensitivity below -100 dBm, which is .0000000000001 watts. Quite low, although populated areas would rarely have a noise-floor that low.
The amount of energy required to interfere with a microphone is similarly miniscule. Consider TV stations. There is a low power TV transmitter for the Boston area WTMU eleven miles from the RF Venue lab. It broadcasts at about 11.2 kW, which comes out to, roughly, a received power outside the lab of -38 dBm. Less than a thousandth of a watt! And yet more than enough to interfere with a microphone signal at normal stage distances.
The above illustration was done assuming both receiver and transmitter are using low gain antennas of 3 dB. But what if we upped that a little? As a reminder, antenna gain does not increase transmitter power, but it can increase the amount of power that arrives at the receiver by “focusing” the energy instead of letting it spread out. Adding a 9 dB directional antenna to the receiver in the same scenario results in an dramatically increased working range, all other factors being equal. Take a look below and compare it to the diagram above.
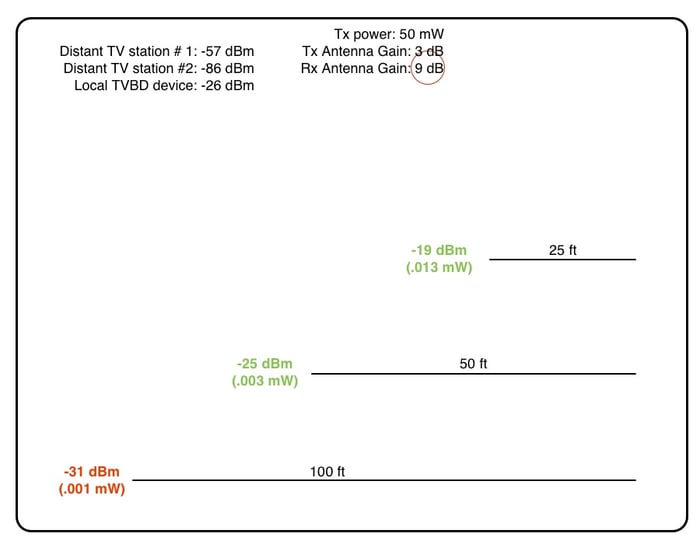
Technically, you do not need to move the receiver closer to the microphone to get these benefits. You only need to move the receiving antenna closer. Many will do this, by extending their antennas on lengths of cables to get closer to the stage. But there is a significant trade-off. Signal strength is lost inside cables as well. The amount of signal lost (attenuated) depends on the grade of cable used and the frequency. We wrote more on this here, and here.
Leading image courtesy Rick Rokely.
Tag(s):
Alex Milne
Alex Milne was Product Marketing Manager and Digital Marketing Manager for RF Venue, and a writer for the RF Venue Blog, from 2014-2017. He is founder and CEO of Terraband, Inc., a networking and ICT infrastructure company based in Brooklyn, NY., and blogs on spectrum management, and other topics where technology,...
More from the blog

COMBINE4 Transmitter Combiner
Contemporary NORTHchurch.tv Improves Wireless with Antenna Distribution
4 min read
| February 7, 2015
Read More

Knowledge Guides
13 Simple Tools Under $100 That Seriously Improve Wireless Audio Performance
17 min read
| November 18, 2015
Read More

CP Beam Antenna
How Location Sound Operators Can Improve Wireless Microphone Reception with Directional Antennas
4 min read
| December 14, 2014
Read More
Subscribe to email updates
Stay up-to-date on what's happening at this blog and get additional content about the benefits of subscribing.

